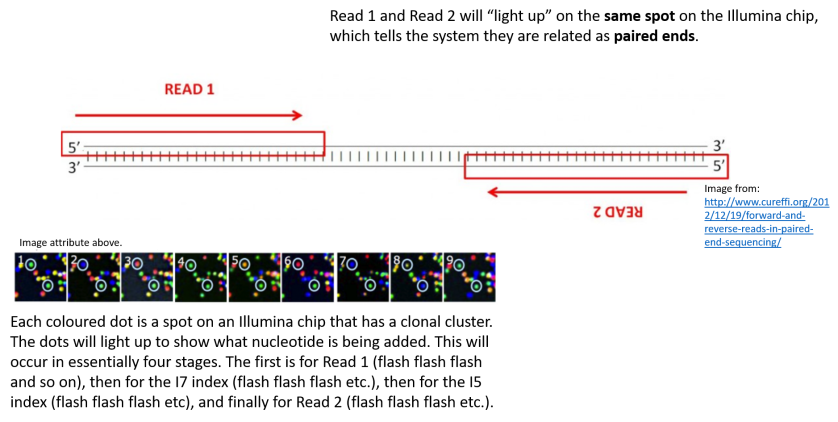
paired end sequencing r1 and r2
So while R1 starts with your 5 adapter for R2 anything is possible depending on the length of the fragment of interest and the read length. Heres what the options look like without running it on our files.

Trouble With Merging Paired End Reads User Support Qiime 2 Forum
There are two FastQ files generated in an Illumina paired-end reads sequencing run.

. If you have multiples of R1 and R2 you can merge the R1 files together. For a single-read run one Read. 2 shows the proportion of low quality R2 reads additional base mismatches in the R2 read relative to the R1 read is correlated with the amount of fragments.
I recently finished mapping an RNAseq run using STAR230 and noticed the read1 and read2 counts are different according to samtools flagstat. There are four fastq files and are named like this. The files have this naming convention.
I received paired-end illumina data for some DNA sequencing Hiseq. This is quite common in single-cell RNA-seq. Typically denoted by R1 and R2 in name of file ie.
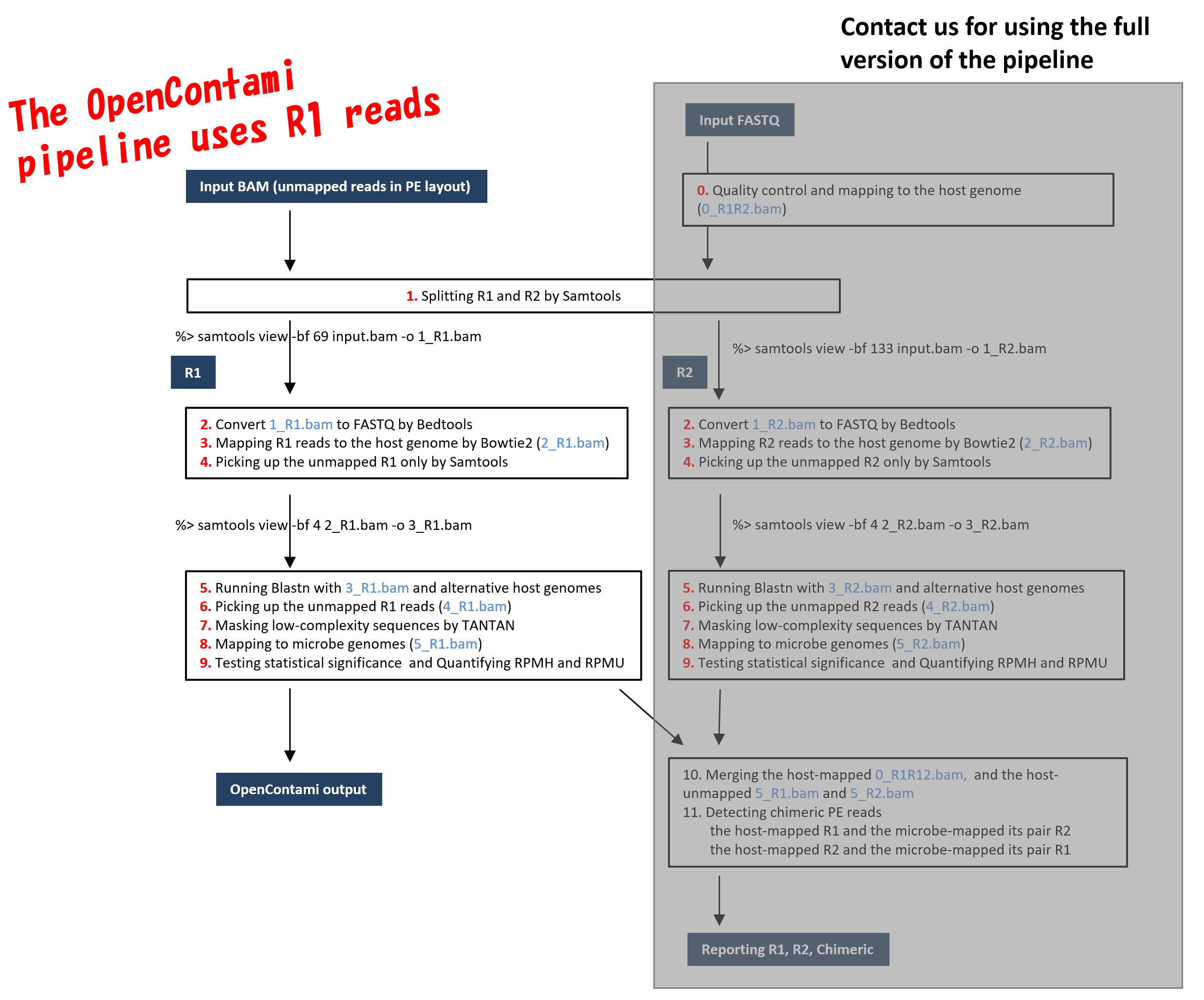
10-09-2013 1013 AM. The map is 80 but the R1 R2 counts. The diagrams show the paired-end reads R1 R2 derived from sequencing DNA fragments white boxes with sequencing adapters gray boxes.
If samples were not multiplexed the demultiplexing step does not occur and for each flow cell lane all clusters are assigned to a single sample. You could see the reverse. The Illumina paired-end sequencing technology can generate reads from both ends of target DNA fragments which can subsequently be merged to increase the.
If the sequencing sample is the same as the original copy the read R1 should be mappable in forward direction in. First sequencing can either be single-end where each sample has only sequence data or paired-end where each sample has two sequence data R1 and R2. The direction and positional order of the paired-end reads R1R2.
When you run cutadapt you give it the adapter sequence to trim and this is different for R1 and R2 reads. If youre running MiSeq Reporter 23 theres a new setting called StitchReads that can do this for you. My understanding is that paired end reads from the Illumina HiSeqMiSeq platforms looks something like this.
For a Paired end reads you would have libraries that are constructed of fragments in both directions but they are never on the same bead and only one continuous read. The steps below can be used if. Simply add StitchReads 1 to your Settings.
Analysis modes of NGmerge. Where xxx is a. As indicated in the comments yes you can definitely tell standard Illumina sequencers to sequence mates in a pair to different lengths.
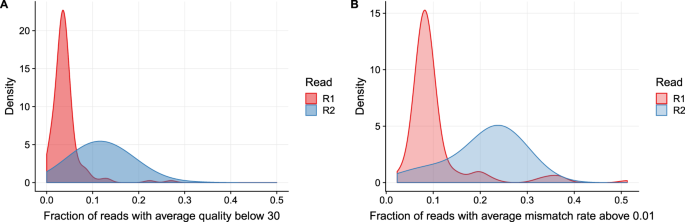
Long Fragments Achieve Lower Base Quality In Illumina Paired End Sequencing Scientific Reports
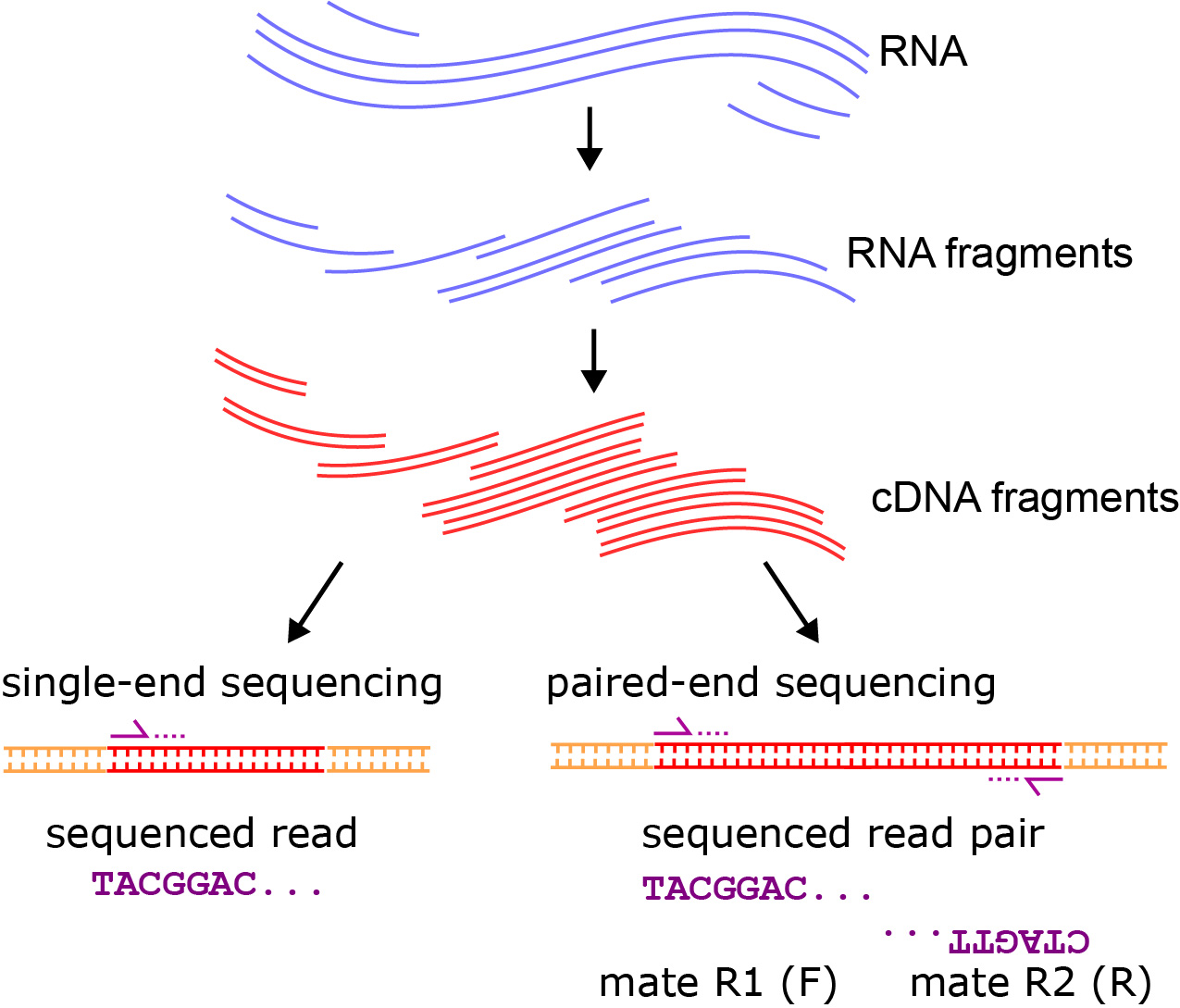
Chapter 6 Transcriptomics Applied Bioinformatics
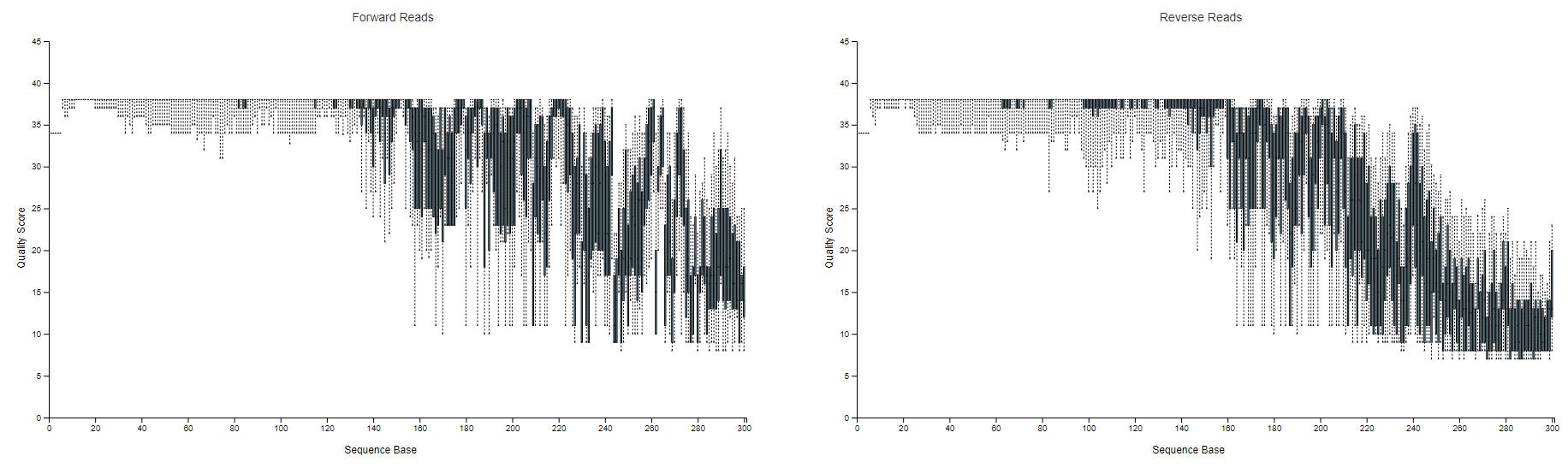
I Wonder What You Suggest When Sequence Quality Drops Off Markedly Before The R1 And R2 Reads Will Overlap User Support Qiime 2 Forum
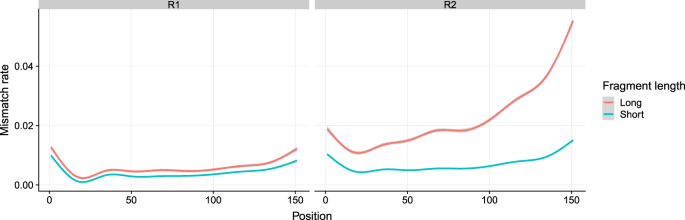
Long Fragments Achieve Lower Base Quality In Illumina Paired End Sequencing Scientific Reports
Paired End Vs Single Read Sequencing Technology

Long Fragments Achieve Lower Base Quality In Illumina Paired End Sequencing Biorxiv

Single End Reads E Paired End Reads Breda Genetics Srl
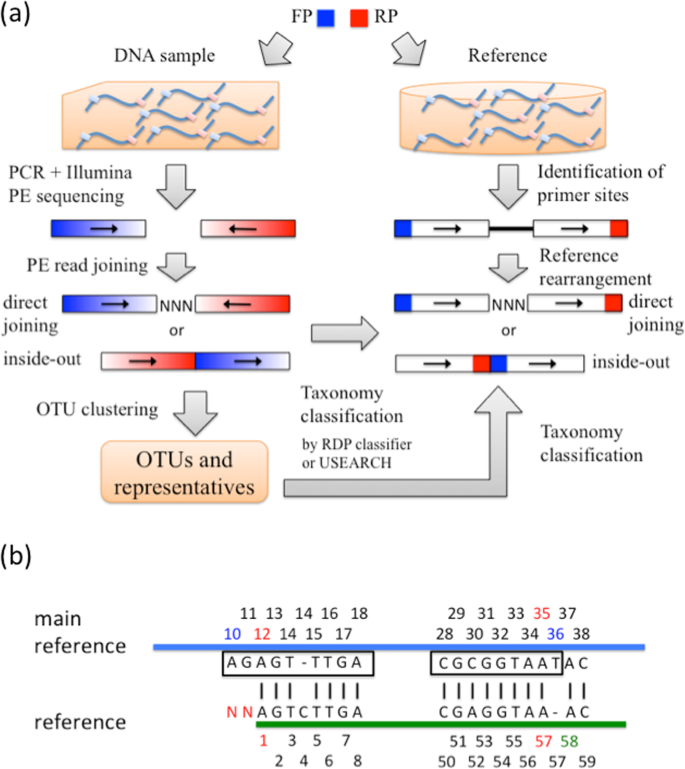
Joining Illumina Paired End Reads For Classifying Phylogenetic Marker Sequences Bmc Bioinformatics Full Text

Deal With Single End And Paired End Data Bioinformatics
The Mgh Nextgen Sequencing Core Core Services
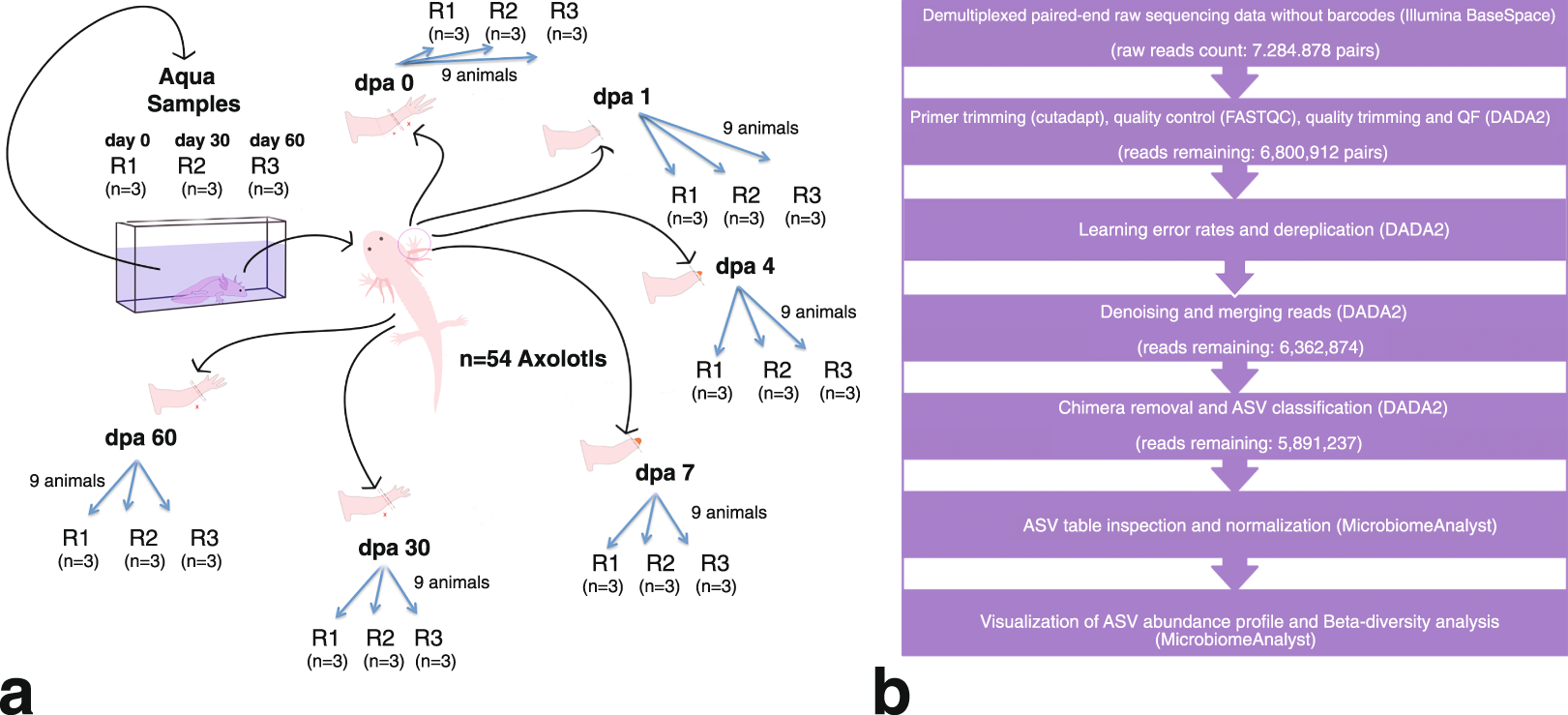
Longitudinal 16s Rrna Data Derived From Limb Regenerative Tissue Samples Of Axolotl Ambystoma Mexicanum Scientific Data
Illumina Sequencing For Dummies An Overview On How Our Samples Are Sequenced Kscbioinformatics
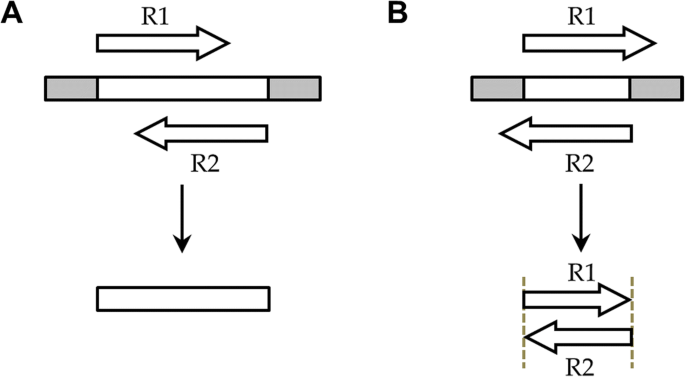
Ngmerge Merging Paired End Reads Via Novel Empirically Derived Models Of Sequencing Errors Bmc Bioinformatics Full Text

Fastqc Illumina Inc Bioz Ratings For Life Science Research

Dmx With 4 Initial Read Files I1 I2 R1 R2 User Support Qiime 2 Forum

Mining For Structural Variations In Next Generation Sequencing Data Semantic Scholar
Introduction Epest Chip Exo Paired End Sequencing Processing Toolkit 1 0 Documentation
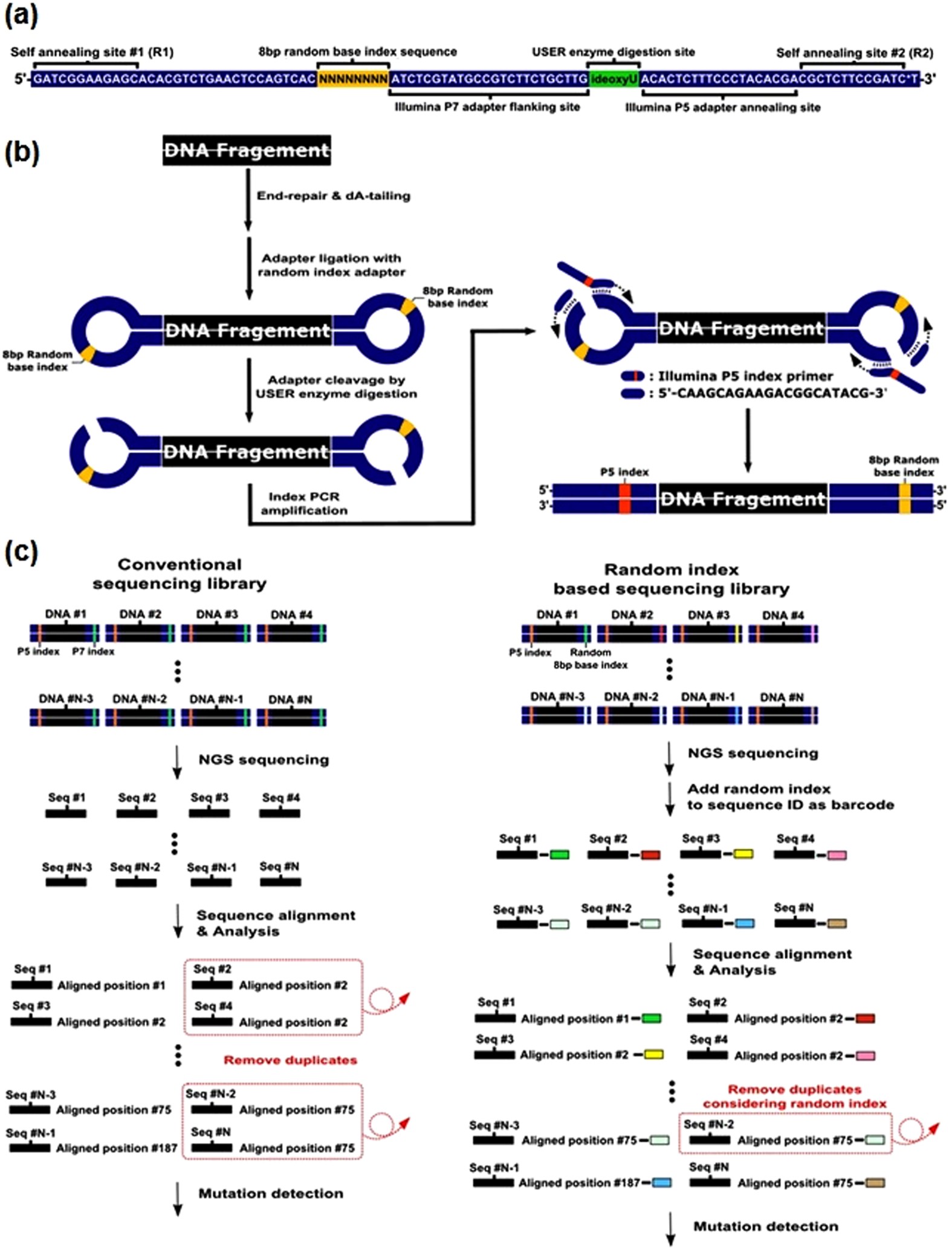
Asymmetrical Barcode Adapter Assisted Recovery Of Duplicate Reads And Error Correction Strategy To Detect Rare Mutations In Circulating Tumor Dna Scientific Reports